thrips life cycle pdf
It feeds on the leaves and within a few days will molt to a larger second stage Instar II that feeds more extensively on the plant. Onion thrips feed by puncturing the epidermis with a stout mandible puncturing deeper mesophyll cells with a fine pair of stylets maxillae and sucking out the cell contents.
Thrips Identification Thrips are difficult to identify to species.
. The life cycle is completed in about 15 days. It is virtually impossible to distinguish flower thrips from. The entirely life cycle of onion thrips can be completed in about three or four weeks during the summer and multiple generations occur on onions.
Egg larval pre-pupal pupal and adult. In Hoya thrips attack and eventually kill the buds Fig. 2 lifecycle diagram.
EggÆ2 Nymphs feed on plantÆ2 quiescent Nymphs ÆWinged Adult. Females can live up to 45 days and lay oviposit between 150. Adults have narrow wings fringed with hairs and can drift long distances in the wind Fig.
General thrips life cycleAdult female thrips use their sharp ovipositor to insert eggs into the tissue of the cotton plant. The life cycle of thrips includes an egg two larval stages that actively feed followed by two or three non-feeding pupal stages Fig. Some species are easier to distinguish by color and host but others require identification by a specialist.
The egg will normally hatch within a couple of days after being laid and the stage that follows Instar I is tiny and wingless. Thrips florum Schumtz is a common pest of gardenia Gardenia jasminoides Ellis flowers in Hawaii. Regarding the life cycle of these thrips eggs are inserted into plant tissues.
General thrips life cycleAdult female thrips use their sharp ovipositor to insert eggs into the tissue of the cotton plant. The distribution was thought to be limited to the west of the Mississippi River before 1980. In most areas thrips appear on growing plants throughout the year.
Thrips life cycle pdf Distribution. Immature thrips larvae are similar in Fig. The life cycle of thrips includes an egg two larval stages that actively feed followed by two or three non-feeding pupal stages Fig.
Their life cycle consists of an egg nymph pre-pupa pupa and an adult. In addition to these stages Tubuliferan thrips have a second pupal stage. Typically hundreds of thrips infest each flower and their feeding and egg laying punctures result in a brown discoloration of the white petals.
LIFE CYCLE OF PEST THRIPS The general life cycles of Terebrantian thrips are simi-lar to one another. Life cycle of thrips comprises four immatur e stages namely first instar and second instar larvae Nymphs pr e-pupa and pupa. However time from egg to adult depends on temperature with the optimum range between 26 and 29C 79 and 84F.
The life cycle and biology of this pest was studied on gardenia flowers to facilitate. Adult thrips live for. There are two larval stages which together last from 8 to more than 20 days.
This thrips feed on almost all. The life stages consist of the egg two active feeding larval instars two quiescent non-feeding instars the propupa and pupa and the adult. The life cycle of thrips consists of the egg stage followed by two larval stages two pupal stages and finally the adult stage Figure 1.
The rate of development strongly depends on temperature. Hatching takes place in 5-8 days. Western flower thrips complete their life cycle from egg to adult in approximately 10 days at 80 F.
Females lay their eggs singly. The average lifetime of a thrip is one month during which it undergoes the following different stages of life-cycle. Thripidae females use.
In general the life cycle egg to adult takes two to three weeks to complete. Thrips lay two to ten eggs per day which require an optimum temperature of 20⁰C and suitable environmental conditions to develop properly into an adult thrip in 20 days. Under these conditions the life cycle may be completed in seven to 13 days.
Eggs are often laid into plant tissue stems leaves flowers or fruit but some species lay their eggs on the plant surface. Nymphs ar e similar to adults but ar e without wings. In the thrips life cycle egg-to-adult.
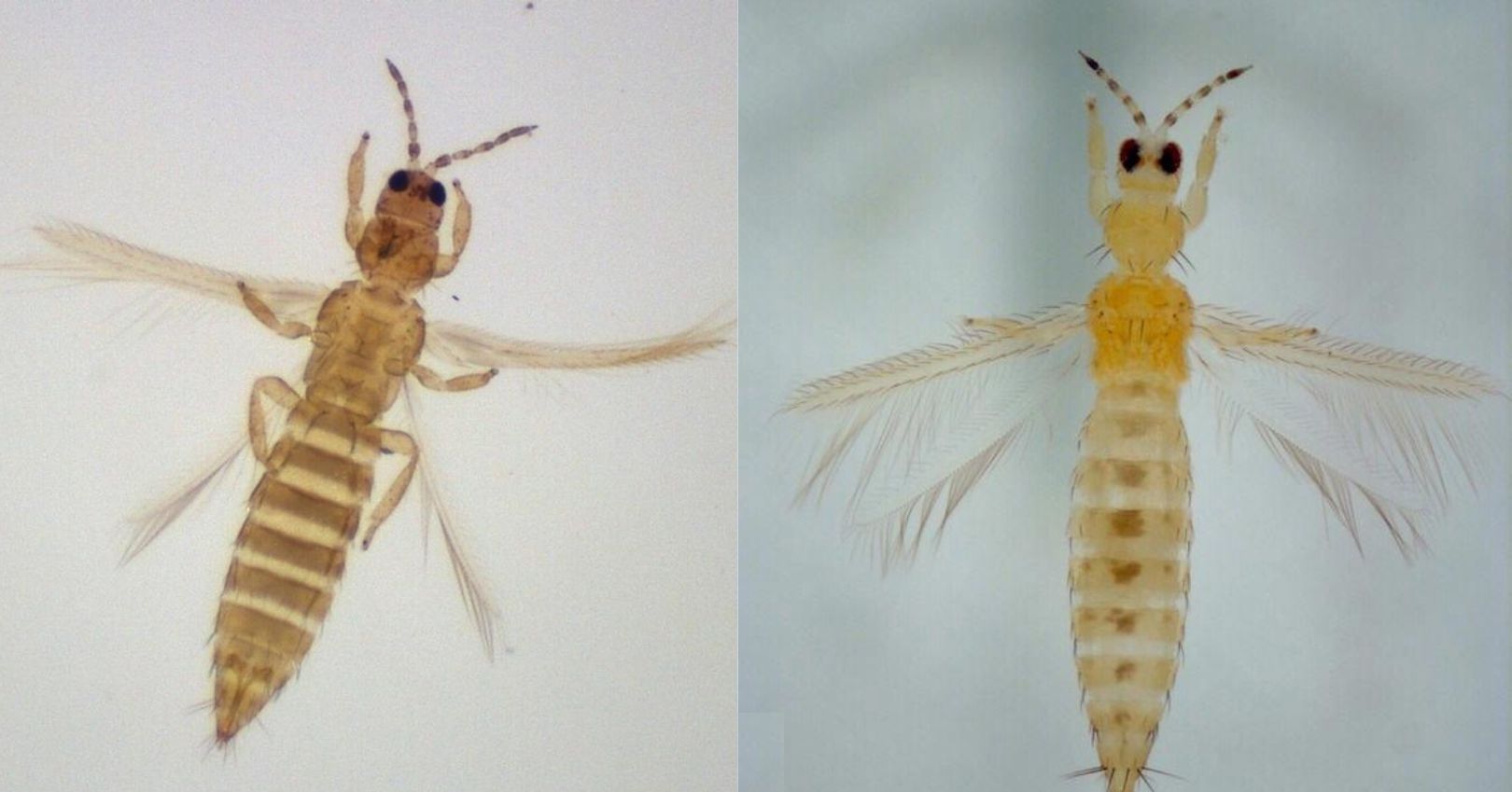
They have piercing and sucking cone-shaped mouthparts. Among the most common and damaging species of pest thrips are Thrips tabaci onion thrips and Frankliniella occidentalis Western flower thrips. The exact time required for thrips to complete their life cycle varies with species temperature and the host plant.
Nymphs move down to the soil and pupate in the top 8-18 cm. However this thrips has become the most prevalent species attacking greenhouse flowers throughout the United States and Canada and many countries in Europe and Asia. Thrips complete their life cycle from egg to adult in approximately 10 days at 80 F 27 C.
Eggs hatch within 3 to 20 days. Thrips are members of the insect Order Thysanoptera. The thrips then enters the nonfeeding prepupal stage.
Thrips are slender cigar-shaped straw-colored insects about 115-inch-long Fig. Eggs are often laid into plant tissue stems leaves flowers or fruit but some species lay. Adults insert eggs in leaf tissue.
Eny 882 In1078 Thrips In Florida Strawberry Crops

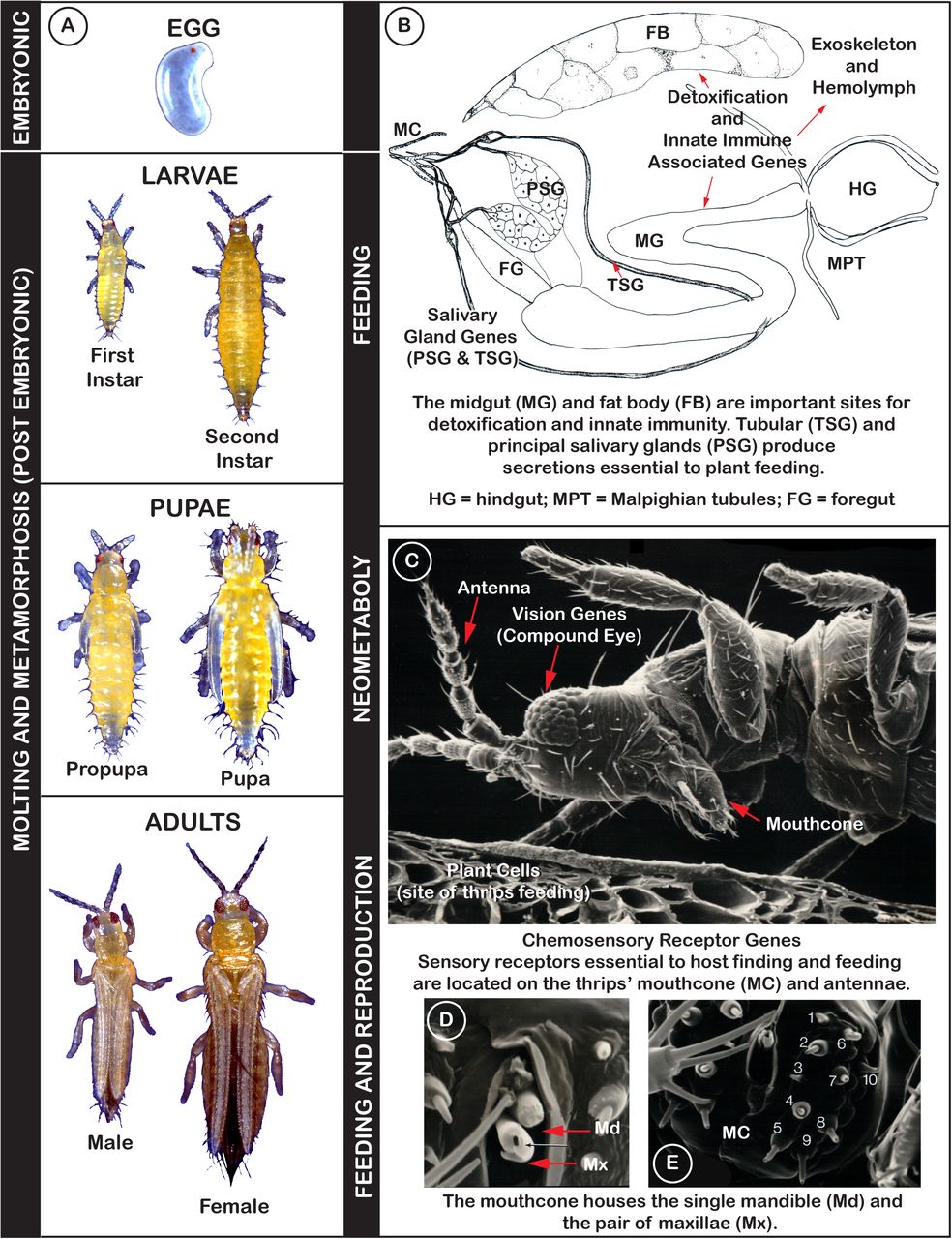
Genome Enabled Insights Into The Biology Of Thrips As Crop Pests Biorxiv

Critters Down Under Thrips Pro Mix Greenhouse Growing

Onion Thrips Wisconsin Vegetable Entomology

Biology And Management Of Thrips Affecting The Production Nursery And Landscape Uga Cooperative Extension
E Journal Of Entomology And Biologicals Agriculture And Natural Resources Blogs

High Tunnel Management Thrips Usu

Chilli Thrips Photos And Research University Of Florida Mrec

Thrips Identify And Get Rid Of Thrips Control Garden Pests The Old Farmer S Almanac

Horticulturae Free Full Text A Comprehensive Thrips Species Assessment For Eco Consistent Management Of Infestations In Mediterranean Citrus Crops Html
Thrips In Greenhouse Crops Biology Damage And Management
E Journal Of Entomology And Biologicals Agriculture And Natural Resources Blogs






